Energy is the life blood of any modern society. We use energy in every walk of life. Without it, our lives would come to a standstill.From the moment we wake up in the morning with an alarm clock until we retire to bed in the night, we use energy for almost everything we do, like the food we cook, the transportation we use to commute, the kitchen appliances and gadgets we use at home and computers we use at office, all of them requires energy to operate.
Energy is a property of matter that can neither be created nor destroyed, however can be converted from one form to another. The source of energy is divided into two groups renewable and non renewable.
Renewable sources which include hydropower, solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, etc never deplete i.e., replenishes over and over again. The most important advantage of renewable source is limited or no emission which helps is reducing the global warming. The renewable energy sources are converted in to electricity or thermal energy.
Non renewable sources examples include petroleum, diesel, coal, natural, gas, nuclear fission (uranium) cannot be replenished in short period of time. The non renewable energy sources are converted to electricity or mechanical energy.
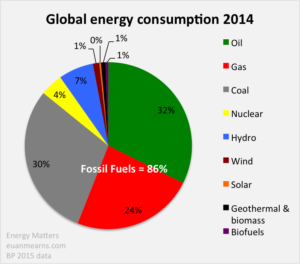
Around 80 % energy used by humans today is derived from the non renewable sources called fossil fuels (Click Here),However the emissions due to use of fossil fuels raises serious environmental concerns.
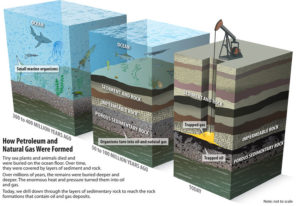
The fossil fuels were formed over a millions and millions of years ago by the action of heat from the earth’s core and pressure from rock and soil on the remains of dead plants and animals. The fossil fuels formed over a million years, are not distributed uniformly over the earth’s surface. Depending on the climate conditions millions of years ago, certain parts of the land masses were favorable for organic matter to grow and thrive.
Unlike renewable sources, the fossil fuels require considerable processing to remove impurities and separate high calorific value fuels for efficient conversion and ease of use. Humans have invented and used various technologies to explore, produce and process the fossil fuels to harness the power of the fossil fuels. This blog shall focus on the oil and gas industry topics.
The oil and gas industry is segmented and organized according to business segment, assets or function as follows:-
- Upstream is also known as Exploration & Production (E&P), deals with recovering and producing crude oil and natural gas. The upstream segment is all about wells.
- Midstream – covers facilities and processes between upstream and downstream. The facilities include processing, storage and transportation of crude oil and natural gas.
- Downstream – provides thousands of products to end user customers around the globe. The products include gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, heating oil, lubricants, synthetic rubber, plastics, fertilizers, pesticides, etc.

Image Source:
| World Consumption Fossil Fuel | Energy Matters |
| Renewable Vs Non Renewable | Fox Hugh |
| Oil and Natural Gas Formation | Socratic.Org |
| Upstream Midstream Downstream | Seeking Alpha |
| Featured Image | Inside Energy |

