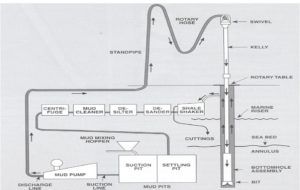
Virtually all oil and gas wells today are drilled using the rotary drilling method. The rock is broken in to small parts or cuttings under the weight applied to a drilling bit. The major components required to drill a wellare as follows:-
- Drill Pipe – To descend the drill bit down the drilled hole.
- Kelly or Top Drive – To rotate the drill pipe and in turn the drill bit.
- Derrick – To hold the drill pipe in place.
- Draw Works – To raise or lower the drill pipe.
- Cutting Tool – also known as drill bit to drill the hole
- Drilling Mud – To act as a media to remove cuttings.
DRILL PIPES
Drill pipe, is hollow, thick-walled, steel or aluminium alloy piping that is used on drilling rigs. It is hollow to allow drilling fluid to be pumped down the hole through the bit and back up through the annulus. Drill pipes include Standard drill pipes (make up majority of the drill string) and Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP). HWDP is a tubular pipe that adds weight or acts as a transitional piece in the drill string.
Drill pipes in general shall conform to API SPEC 5DP and are manufactured in Grades E, X, G and S. Drill pipes are manufactured in proprietary grades as well for sour service and critical service which exceeds the specifications set forth in API SPEC 5DP. The two most important dimensional specification of drill pipes are length and diameter. Each segment/length of drill pipe referred to as a “Single” is classified by API into three distinct ranges R1 (18 to 22 ft), R2 (27 to 31 ft) and R3 (36 to 45 ft). The outer diameter (OD) of the drill pipe ranges from 2 3/8” to 6 5/8”. The ratio of drill pipe OD to borehole diameter is recommended to be about 0.6
Each end of the drill pipe incorporates a tool joint, differentiated by male threaded connection on one end referred to as ‘PIN’ and the female threaded connection on the other end referred to as ‘BOX’. These are prefabricated and welded to the pipe ends. Common API tool joints include Regular (REG), full hole (FH) and Internal Flush (IF). Tool joints are specified by upset (IU, EU or IEU) and  thread type specified by threads per inch (TPI) and it’s taper.
thread type specified by threads per inch (TPI) and it’s taper.
Drill collars are a component of the drill string that makes up part of the Bottom Hole Assembly (BHA) which are primarily used to weigh down the drill bit to dampen vibration and impact forces. The drill pipes, drill collars and drill bit assembled together is called a Drill String or Column. The drilling fluid is pumped in to the drill string via the mud pumps to the bottom of the hole to remove the cuttings. The torque is applied to the drill bit to remove the earth rock via the kelly or top drive.
KELLY OR TOP DRIVE
Kelly or Top Drive is the drilling equipment which transfer both rotational and compression force to the bit in order to make a hole. The main parts that make up a kelly drilling system are: the swivel, kelly, kelly bushing, master bushing, and the rotary table. The swivel is attached to the hook of the traveling block and enables the drill string to rotate. The kelly is square or hexagonal portion of pipe, which fits snugly inside the kelly bushing, which in turn fits snugly into the master bushing. The master bushing is located on the rotary table and rotates with the rotary table as it turns.
The kelly bushing contains four studs that stick out on each corner of the bushing, enabling it fit snuggly and securely inside the master bushing. Thus, as the rotary table turns, the master bushing rotates, which in turn rotates the kelly bushing, kelly, as well as the rest of the drill string. After a single joint of drill pipe has passed through the rotary table, a connection of another joint of drill pipe must be made in order for more pipe to be lowered into the hole. The kelly rig’s inability to handle more than one joint of pipe at a time is the main disadvantage when compared to the more innovate rigs equipped with top drives which are discussed below.
A top drive rig utilizes a heavy duty powered swivel which contains an internal motor enabling the top drive to grip onto and rotate the drill pipe on its own, without the need for a kelly to provide rotation. The top drive motor turns a threaded drive shaft which connects directly onto the top of the drill string to rotate it. Although a rig equipped with a top drive still needs a rotary table and slips to keep the drill string from falling into the hole when making a connection, a top drive eliminates the need for traditional rotary equipment such as a kelly and kelly bushing.
Unlike traditional kelly rigs, many rigs equipped with a top drive are able to handle stands (2-3 joints) of drill pipe, up to 90 feet in length at a time. This ability to handle multiple joints of drill pipe at a time increases the drilling rate and increases efficiency significantly. When a connection must be made, the driller simply pulls up the drill string until the bit is off the bottom and turns off the mud pumps. The crew then sets the slips in the rotary table to hold the drill string in place while the top drive is hoisted up to the top of the derrick to grasp the next stand of drill pipe to be added. Once the new stand of pipe is connected, the driller turns the pumps on, the crew removes the slips, and drilling can continue. The following video provides an overview of the kelly and topdrive.
DERRICK
A derrick is a lifting device composed at minimum of one guyed mast, as in a gin pole, which may be articulated over a load by adjusting its guys. Most derricks have at least two components, either a guyed mast or self-supporting tower, and a boom hinged at its base to provide articulation, as in a stiffleg derrick.
The most basic type of derrick is controlled by three or four lines connected to the top of the mast, which allow it both to move laterally and cant up and down. To lift a load, a separate line runs up and over the mast with a hook on its free end, as with a crane.
There are various types of derrick based on how the tower or mast is set up and the use of boom which includes A-Frame, Basket, Breast, Chicago Boom, Gin Pole, Guy, Shearleg, and Stiffleg. For more details visit Wikipedia
DRAW WORKS
A draw-works is the primary hoisting machinery that is a component of a rotary drilling rig. Its main function is to provide a means of raising and lowering the traveling blocks. The wire-rope drilling line winds on the drawworks drum and extends to the crown block and traveling blocks, allowing the drill string to be moved up and down as the drum turns. For detailed explanation visit Wikipedia.

Drawworks can be used to hoist or lower several hundred thousand pounds of weight and can come in AC, DC or mechanical power units. Horsepower ratings for drawworks can also have a wide range, often ranging from 1000 HP to over 3000 HP.
CUTTING TOOL – DRILL BIT
The bit is made up on (i.e., screwed into) the end of a drill string . The ideal drilling bit is selected based on the drilling cost per foot, drillability, abrasiveness, type of reservoir, cost of the bit and depth. The drill bits are mainly classified as Drag Bit and Rolling Cutter Bits

Drag Bit (Fixed Cutter Blades)
Consist of fixed cutter blades that are integral with the body of the bit and rotate as a unit with drill string. Bits include steel cutters, diamond or PDC (Polycrystalline Diamond Compact).
Steel cutter bits are serrated steel blades set at different angles (eg fishtail bit). Best for soft, uniform and unconsolidated formations. Now being replaced by other types.
Natural diamond bits – the face or crown of the bit consists of many diamond set in a tungsten carbide matrix. Achieves penetration rates of rock bit up to 10 ft/hr for hole diameter up to 6 inches. Best for hard non brittle formations, Types include soft formation and hard formation diamond bits
PDC bits consists of a layer of synthetic PD about 1/64” thick bonded to a cemented tungsten carbide in a high pressure high temperature process. It contains many diamond crystals bonded together. Best in soft, firm and medium hard, non abrasion formations.
TSP bits (Thermally stable polycrystalline) are similar to PDC but are tolerant of much higher temperature than PDC.
Rolling Cutter Bits (Rock Bits with Cones)
Two or more cones contains the cutting elements which rotate about the axis of the cone as the bit is rotated at the bottom of the hole. The 3 cone rolling cutter bit is by far the most common. Large variety of tooth design and bearing types. Increased drilling speed but tooth wears faster (4 for soft and 0 for hard). Any formation for can be handled, handles changes in formation, acceptable life and drilling rate and reasonable cost
Steel Tooth (Milled Tooth Bit ) – long teeth for soft formations, shorter teeth for harder formations, self sharpening teeth by using hard facing on one site, high drilling rates in softer rocks
Carbide Tooth (Tungsten Carbide Insert Bit) provides long life cutting structure in hard rocks, hemispherical inserts for very hard rocks, larger or more pointed inserts for softer rock, handles high bit weights and high rpm, inserts fail through breakage rather than wear.
The performance attributes of various types of drill bit are tabulated as below.
| Performance Attribute | Milled Tooth Bits (MT) | Tungsten Carbide Inserts (TCI) | Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC) | Diamond | Diamond Impregnated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Utilization by Footage | 10% | 15% | 70% | 2% | 3% |
| Application | Soft and sticky Hard formations |
Soft and sticky Hard formations |
Hard formations Directional wells Long wells Shale formations |
Hard formations Directional wells Long wells |
Hard & Abrasive formations |
| Rate of Penetration | High in soft formations | High in soft formations | High in sand, Shale, Clay and Siltstone | High in sand, Shale, Clay and Siltstone | High in sand, Shale, Clay and Siltstone |
| Cost | Low | Low | Medium to High | High | High |
| Wearing Damage Risk | Medium to High | Medium to High | Low to Medium | Low to Medium | Low to Medium |
DRILLING MUD
DRILLING MUD is the fluid pumped down the inside of the drill pipe and exits the drill bit. It is complete mixture of fluids, solids and chemicals that must be carefully tailored to provide the correct physical and chemical characteristics required to safely drill the well. Fluid goes through shakers which strain the cuttings from good fluid which is returned to the pit. The drilling mud is classified in to two types:
Oil based mud composed of oil as the continuous phase and water as the dispersed phase in conjunction with emulsifiers and wetting agents. The oil base can be diesel, kerosene, fuel oil or selected crude oil. Expensive but worth the cost when deep drilling and high temperature holes that dehydrate water based mud. Also water soluble zones can be drilled.
Advantages of oil based mud include High drilling rates, improved lubrication, anti corrosive properties and maintains formation at high temperatures.
Oil based mud can cause toxic fumes that affect the drilling team it can also cause damage to well bore / surrounding formation due to high density / pressure, contaminates areas of fresh water aquifiers, disposal of cuttings in an appropriate place to avoid environmental contamination.
Water based mud systems begin with water, then clays and other chemicals are incorporated in to the water to create a homogenous blend resembling something like chocolate milk referred as GEL. Canbe used as coolant of the drill bit which is required rather than lubrication.
Advantages of water based mud includes non use of hydrocarbon which reduces impact on environment, easy control of viscosity, easy control of density for low pressure formation while drilling and drill chips easily removed from fluid at shakers
Water based mud is not an efficient lubricant as OBM, it can promote corrosion to drill bit. Water based mud is not efficient at high temperatures and does not carry drill chips to the surface as efficiently as OBM.
Image Credits:
Drill Pipe / Drill String / Derrick / Draw Works
Information Sources:
Derrick & Drawworks info source: Wikipedia/
Casing and well completion info source – Slideshare
Drill pipe info source: Globalspec/
Kelly or Top Drive info source: Petro Prophet

